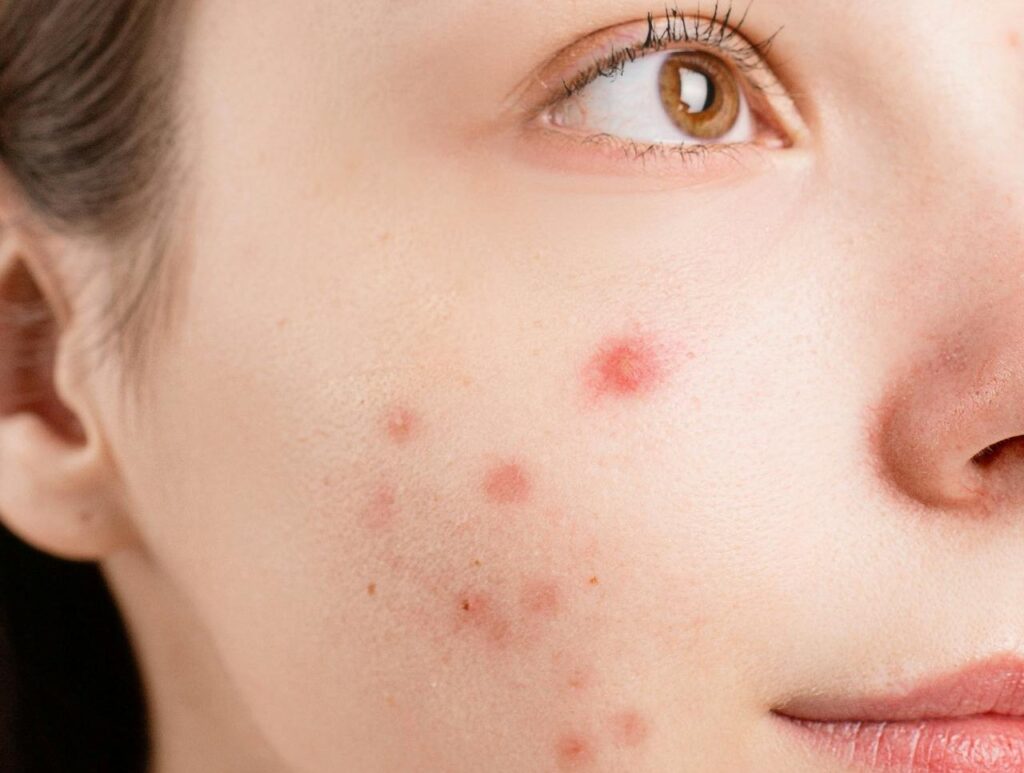
Hormonal acne isn’t just a teenage problem—it’s a reality that affects millions of adults well into their 30s, 40s, and beyond. If you’re dealing with persistent breakouts around your jawline, chin, or cheeks, you’re likely experiencing hormonal acne, a condition that affects up to 50% of women in their twenties and 25% of women in their forties.
Understanding hormonal acne is the first step toward effective treatment. Unlike the random breakouts of adolescence, adult hormonal acne follows predictable patterns and responds to specific treatment approaches. This comprehensive guide will help you identify, understand, and effectively manage hormonal acne at any stage of life.
What Is Hormonal Acne?
Hormonal acne is a type of adult acne directly linked to fluctuations in hormone levels, particularly androgens like testosterone. While all acne involves some hormonal component, hormonal acne specifically refers to breakouts that occur in response to hormonal changes throughout your menstrual cycle, pregnancy, menopause, or other life transitions.
Key Characteristics of Hormonal Acne
Hormonal acne has distinct features that set it apart from other types of breakouts:
- Location: Primarily affects the lower third of the face, including the jawline, chin, and around the mouth
- Timing: Often worsens during the week before menstruation
- Type of lesions: Deep, cystic bumps that are painful and slow to heal
- Persistence: Continues well beyond teenage years, often into the 30s and 40s
- Cyclical nature: Follows a predictable pattern related to hormonal fluctuations
Understanding the Causes of Hormonal Acne
The Role of Hormones in Acne Formation
Hormonal acne develops through a complex process involving four key factors:
- Increased sebum production: Rising androgen levels stimulate oil glands to produce excess sebum
- Clogged hair follicles: Dead skin cells and sebum block pores, creating an environment for bacterial growth
- Bacterial overgrowth: Propionibacterium acnes bacteria multiply in the clogged follicles
- Inflammatory response: Your immune system responds to the bacteria, causing redness, swelling, and pain
Common Hormonal Triggers
Several life events and conditions can trigger hormonal acne:
- Menstrual cycle fluctuations: Progesterone and estrogen changes before menstruation
- Pregnancy: Dramatic hormonal shifts, particularly in the first trimester
- Menopause: Declining estrogen levels and relative increase in androgens
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome): Elevated androgen levels
- Birth control changes: Starting, stopping, or switching contraceptive methods
- Stress: Elevated cortisol levels can worsen hormonal imbalances
- Thyroid disorders: Can affect overall hormonal balance
Why Hormonal Acne Affects Adults of All Ages
Contrary to popular belief, there’s no specific age when hormonal acne stops. Many factors contribute to adult hormonal acne:
Life Stage Factors
- 20s and 30s: Career stress, lifestyle changes, and reproductive years
- 40s and beyond: Perimenopause and menopause hormonal shifts
- Post-pregnancy: Hormonal readjustment after childbirth and breastfeeding
Modern Lifestyle Contributors
- Chronic stress: Elevates cortisol and disrupts hormonal balance
- Poor sleep quality: Affects hormone regulation and skin repair
- Dietary factors: High-glycemic foods and dairy may worsen hormonal acne
- Environmental toxins: Endocrine disruptors in cosmetics and household products
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches for Hormonal Acne
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments form the foundation of hormonal acne management:
Over-the-Counter Options
- Salicylic acid (0.5-2%): Unclogs pores and reduces inflammation
- Benzoyl peroxide (2.5-10%): Kills acne bacteria and prevents new breakouts
- Adapalene (0.1%): Available OTC retinoid that normalizes skin cell turnover
Prescription Topicals
- Tretinoin: Gold standard retinoid for acne treatment
- Clindamycin: Antibiotic gel or lotion for bacterial control
- Azelaic acid: Reduces inflammation and helps with post-acne marks
- Combination products: Tretinoin + clindamycin or benzoyl peroxide + adapalene
Oral Medications
For moderate to severe hormonal acne, oral treatments may be necessary:
Hormonal Therapies
- Spironolactone: Blocks androgen receptors, reducing oil production
- Birth control pills: Certain formulations help regulate hormones
- Metformin: For women with PCOS-related acne
Other Oral Options
- Antibiotics: Doxycycline or minocycline for inflammatory acne
- Isotretinoin: For severe, treatment-resistant cases
- Anti-inflammatory supplements: Omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, spearmint tea
Professional Treatments
Dermatological procedures can enhance topical and oral treatments:
- Chemical peels: Salicylic acid or glycolic acid peels
- Light therapy: Blue light or photodynamic therapy
- Cortisone injections: For large, painful cysts
- Extraction procedures: Professional removal of blackheads and whiteheads
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Management
Optimizing Your Skincare Routine
A gentle, consistent skincare routine is crucial for managing hormonal acne:
Morning Routine
- Gentle cleanser with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide
- Lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer
- Broad-spectrum SPF 30+ sunscreen
Evening Routine
- Double cleanse if wearing makeup
- Treatment product (retinoid or prescribed medication)
- Hydrating, non-comedogenic moisturizer
Dietary Considerations
While diet alone doesn’t cause hormonal acne, certain modifications may help:
- Reduce high-glycemic foods: Limit refined sugars and processed carbohydrates
- Consider dairy reduction: Some people see improvement when limiting dairy
- Increase anti-inflammatory foods: Omega-3 rich fish, leafy greens, berries
- Stay hydrated: Adequate water intake supports overall skin health
Stress Management Strategies
Chronic stress significantly impacts hormonal balance:
- Regular exercise: Helps regulate hormones and reduce stress
- Adequate sleep: 7-9 hours nightly for optimal hormone production
- Mindfulness practices: Meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises
- Professional support: Therapy or counseling for chronic stress
Prevention Strategies and Long-Term Outlook
Hormonal Testing and Monitoring
Consider working with healthcare providers to:
- Evaluate hormone levels: Test for PCOS, thyroid disorders, or other imbalances
- Monitor treatment progress: Regular check-ins to adjust medications
- Address underlying conditions: Treat root causes of hormonal imbalances
Setting Realistic Expectations
Understanding treatment timelines helps maintain realistic expectations:
- Initial improvement: 6-8 weeks for topical treatments
- Significant results: 3-4 months for oral medications
- Maintenance phase: Ongoing treatment often necessary to prevent recurrence
When to Seek Professional Help
Consult a dermatologist if you experience:
- Severe, cystic acne that doesn’t respond to OTC treatments
- Acne causing scarring or significant emotional distress
- Sudden onset of adult acne without clear triggers
- Signs of hormonal imbalances (irregular periods, excessive hair growth)
Cost Considerations and Insurance Coverage
Many insurance plans cover:
- Dermatologist consultations for acne treatment
- Prescription medications for moderate to severe acne
- Some professional treatments when medically necessary
The Psychological Impact and Mental Health Support
Hormonal acne can significantly impact self-esteem and mental health. Remember:
- You’re not alone: Millions of adults struggle with hormonal acne
- Treatment takes time: Be patient with the process
- Seek support: Consider counseling if acne affects your quality of life
- Focus on overall health: Acne doesn’t define your worth or beauty
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can hormonal acne be cured permanently?
A: While there’s no permanent “cure,” hormonal acne can be effectively managed with the right treatment approach. Many people achieve long-term clear skin with consistent treatment and lifestyle modifications.
Q: How long does it take to see results from hormonal acne treatment?
A: Most people see initial improvement within 6-8 weeks, with significant results appearing after 3-4 months of consistent treatment. Patience is key, as skin cell turnover takes time.
Q: Is it safe to use retinoids for hormonal acne during pregnancy?
A: Most retinoids are not recommended during pregnancy. Consult your healthcare provider about pregnancy-safe alternatives like azelaic acid or certain antibiotics.
Q: Can men get hormonal acne?
A: Yes, men can experience hormonal acne, though it’s less common than in women. Male hormonal acne often relates to testosterone fluctuations, stress, or underlying health conditions.
Q: Will my hormonal acne get worse during menopause?
A: Some women experience worsening acne during perimenopause and menopause due to declining estrogen levels. However, proper treatment can effectively manage these breakouts.
Take Control of Your Hormonal Acne Today
Hormonal acne may be persistent, but it’s not permanent. With the right combination of professional treatment, consistent skincare, and lifestyle modifications, you can achieve clearer, healthier skin at any age. Remember that effective treatment often requires patience and may involve some trial and error to find what works best for your unique situation.
Don’t let hormonal acne control your life. Start by implementing gentle skincare practices, consider consulting a dermatologist for personalized treatment options, and remember that clear skin is achievable with the right approach and commitment to treatment.
Your journey to clearer skin starts today—take the first step by choosing one strategy from this guide and committing to consistent implementation. Your future self will thank you for taking action now.